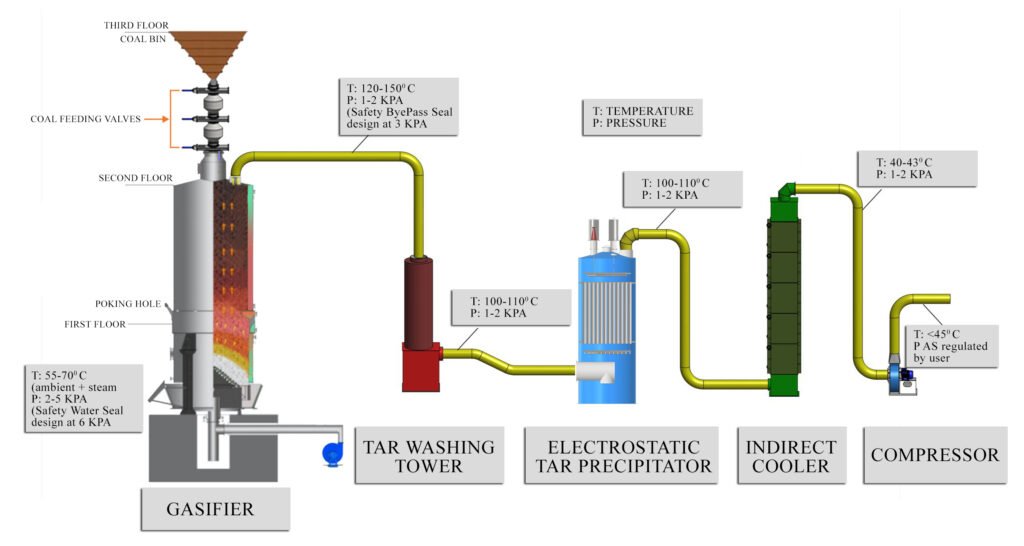
Coal continues to play a
major role in industrial
energy supply, but traditional
usage poses challenges
such as harmful emissions
and health risks. To address
these issues, coal
gasification has emerged as
a cleaner and more efficient
alternative. The process
converts coal into synthesis
gas (syngas) at high
temperatures with limited
oxygen, producing a
versatile fuel with higher
calorific value and reduced
environmental impact.
CASE Group, a technology
provider in this space, has
developed clean cold
gasifiers that operate
through a series of
controlled stages. Coal is
first fed into the hearth via
conveyor belts, undergoing
drying, pyrolysis, reduction,
and oxidation. These
sequential reactions
transform the coal into
producer gas.
The gas then passes
through downstream
cleaning equipment. In the
Tar Washing Tower (TWT),
tar particles are removed
through a seeding process,
reducing the load on
subsequent systems. The
Electrostatic Tar Precipitator
(ESP) applies high-voltage
corona discharge to separate
heavier tar residues, while
the Indirect Cooler (IDC), a
fin-tube heat exchanger,
lowers the gas temperature
to below 45°C. CASE Group
also ensures Zero Liquid
Discharge (ZLD) by treating.
and reusing phenolic
wastewater generated during
the process.
The resulting clean
syngas can be compressed
and supplied for use across
industries including
steelmaking, rolling mills,
pellets, ceramics, and more.
Even the ash residue from
gasifiers finds utility in brick
manufacturing, contributing
to circular resource use.
With India aiming to reduce
fuel imports and transition
toward greener technologies,
gasification offers a viable
pathway for sustainable
energy use. By providing
cleaner alternatives while
ensuring efficiency, the
technology is gaining wider
acceptance across energyintensive sectors.

